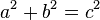the vector horizon closer to home
By Henryk Szubinski

4 freedooms ; the 5th framework: the freedoom of knowledge moovement; Chordis6; the 7th framework
basis on the type MARS possible :
what is a curvature BIT UNIT in quantal trigonometry terms
a basic computations set for the instance of depth probeing relationships with the Marsian surface:

but how would you use this on Mars:
The basics of the set equations for a quantal 1 UNIT value as shared by 10 UNITS in total where there is full efficiency of the usage:
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem (in American English) or Pythagoras’ theorem (in British English) is a relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle (right-angled triangle in British English). It states:
In any right triangle, the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares whose sides are the two legs (the two sides that meet at a right angle).
The theorem can be written as an equation:
where c represents the length of the hypotenuse, and a and b represent the lengths of the other two sides.
The Pythagorean theorem is named after the Greek mathematician Pythagoras, who by tradition is credited with its discovery and proof,[1] although it is often argued that knowledge of the theory predates him. (There is much evidence that Babylonian mathematicians understood the principle, if not the mathematical significance.)
making comparatives with the volumes on the total volumes of both the sections to define the volume remaining and using this total value resultant to divide the velocity of the process where the S value is the remaining quantal value for motion possibilities:
the usage of a H2O basis in the data on the projective basis of the angle of inclinations over the 1 st quadrance into the secondary quadrance as the basis for a alterations of a approximate 100 degree value where the space of the surface indentations are similar by 90 degrees will give you a 10 degree window for the Marsian surface values of the basic quantality of the whole length of the section as divisive with the amount of volume remaining and the volume used as the surface values of the length of the sections and the height = 10 units so that the tan angle = 10 / x
as such the values for the angle of incidence can be seen as the type incline in a angle of motion related to the horizon but also to the vectors towaards the horizon by the basics of trigonometry where pythagoras theorem can be used on wedges into a surface as computatable by the top view only:
Where the angle of alterations to the right angle = 10 / 2 = 5 degrees
in which the data on the process by which a 360 degree vector = 5 = section value amount =70 degrees so that the angle of primary indentations = tan 70 / 2 = 5/x
tan 35 =5/x
on any displacement caused by a 1 unit in relations to 10 UNIT INTERACTIONS:
where the question is which of the two is the H2O the basics of a value closer to the 35 tan = the primary relationship to EARTH values:
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem (in American English) or Pythagoras’ theorem (in British English) is a relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle (right-angled triangle in British English). It states:
In any right triangle, the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares whose sides are the two legs (the two sides that meet at a right angle).
The theorem can be written as an equation:
where c represents the length of the hypotenuse, and a and b represent the lengths of the other two sides.
The Pythagorean theorem is named after the Greek mathematician Pythagoras, who by tradition is credited with its discovery and proof,[1] although it is often argued that knowledge of the theory predates him. (There is much evidence that Babylonian mathematicians understood the principle, if not the mathematical significance.)


Animation showing another proof by rearrangement [5]

Proof of Pythagorean theorem by rearrangement of 4 identical right triangles: Since the total area and the areas of the triangles are all constant, the total black area is constant. But this can be divided into squares delineated by the triangle sidesa, b, c, demonstrating thata2 + b2 = c2.

the MARS 500 project
laying down the lowdown on the nonsense of the stuff for Mars habitable zone defined in relations to a 100 % human function and the 045 % level defined as 1/100 =5 months in approximate values as the type cleft in a Mars feature as the Mars upto a 2/3 as =66.6 % where the basics are a 5 periodic approximate =3 periodic and the computations back into the usage of the formulation:

tan 35 =0.3 /3
=0.1
the basic height of human means on a habitable level effect where
tan 35 =0.1
In object-oriented programming, a protocol or interface is what or how unrelated objects use to communicate with each other. These are definitions of methods and values which the objects agree upon in order to cooperate.
For example, in Java (where protocols are termed interfaces), there is the Comparable interface specifies a method compareTo() which implementing classes should implement. So, this means that a separate sorting method, for example, can sort any object which implements the Comparable interface, without having to know anything about the inner nature of the class (except that two of these objects can be compared by means of compareTo()).
The protocol is a description of:
- the messages that are understood by the object,
- the arguments that these messages may be supplied with, and
- the types of results that these messages return.
- the invariants that are preserved despite modifications to the state of the object
- the exceptional situations that will be required to be handled by clients to the object
If the objects are fully encapsulated then the protocol will describe the only way in which objects may be accessed by other objects.
Some programming languages directly support protocols or interfaces (Objective-C, Java, C#, D, Ada, Logtalk). Older languages may also have features that can support the interface concept, such as abstract base classes with pure virtual functions in C++, or object-oriented features in Perl.
Note that functional programming and distributed programming languages have a concept which is also called a protocol, but whose meaning is subtly different (i.e. a specification of allowed exchangesof messages, emphasis on exchanges, not on messages). This difference is due to somewhat different assumptions of functional programming and object-oriented programming paradigms. In particular, the following are also considered as part of a protocol in these languages:
- The allowed sequences of messages,
- Restrictions placed on either participant in the communication,
- Expected effects that will occur as the message is handled.